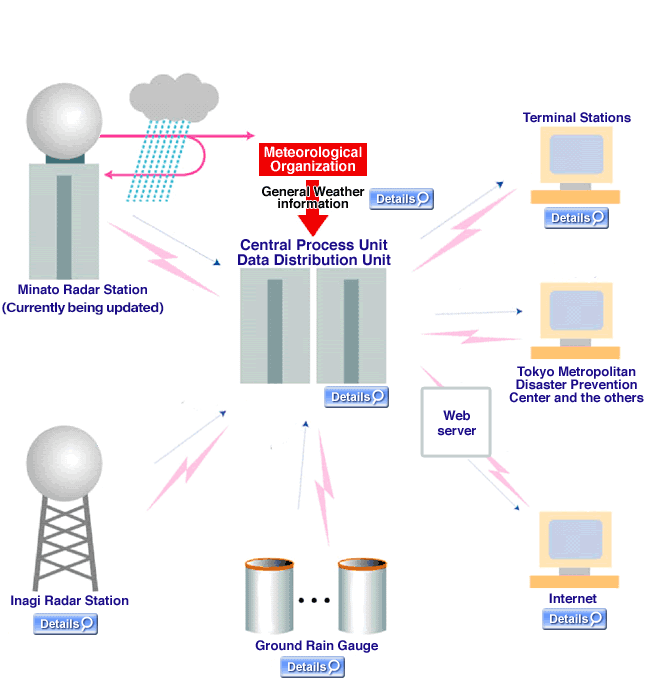
- Radar Rainfall Gauge System
-
A radar beam travels straight and reflects on the surface of an object. The property enables radar to measure the location and the dimension of the object. The Radar Rainfall Gauge system gathers rain signals, omitting the reflection from mountains or structures.
Tokyo Amesh has five radar stations, two in Tokyo (Inagi and Minato) and two in adjoining municipalities*, and some 130 ground gauges.
Based on the measured data of the devices, the central process unit (CPU) calculates the intensity of the rain. CPU sends the result to the data distribution unit(DDU) and, through it, to terminal stations. At a terminal station, the information is given a graphical interface suited to plant operation.
*) Since 2007, Tokyo Amesh has begun to take in the data of adjoining municipalities.
The expansion of measuring devices leads to improvement of precision and reliability.
- General Weather information
- Information from meteorological companies is available along with general weather information, such as lightning strikes frequency or typhoon course, on terminal stations.
- Inagi Radar station
-

The station observes the area over the Tama cities and sends rainfall intensity data to CPU at an interval of one-minute.
- Central Process Unit,
Data Distribution Unit -

After the rainfall intensity data sent from both radar base stations and the rainfall intensity data of Japan Meteorological Agency radar are combined, these data are distributed to each terminal station.
- Ground rain gauge
-

Data observed by surface rain gauge in the sewer station and construction station is transmitted to the central processing unit.
- Internet
- Among the meteorological information, the radar data and the warnings or advisories in Tokyo, is open to the public through Internet Homepage. The update interval is 5 minutes.
- Terminal Station
-

Terminal Station receives the rainfall intensity data processed in CPU and the general weather information to show them in "easy-to-grasp" graphical interface. - Graphical Interface
-

Amesh base screen
Wide-area radar observation
(Nationwide overall monitoring)
Lightning strikes frequency
Typhoon course